Effective Cybersecurity Measures for Industrial IoT Challenges
In recent years, manufacturing industries have undergone significant transformations, driven by rapid advancements in technology. Manufacturers are now integrating IT and OT (operational technology) convergence tools at an accelerated pace to optimize processes and improve efficiency. At the heart of this evolution lie embedded systems—whether small smart sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLC), distributed control systems (DCS), human-machine interfaces (HMI), or edge devices—that are essential in gathering and processing data within the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) ecosystem. Positioned at the foundation of the IIoT hierarchy, these embedded systems often connect to the cloud, either directly or through gateways, enabling real-time data flow and automation.
While the benefits of these interconnected systems are immense, they bring substantial cybersecurity risks. The continuous connectivity of embedded systems expands the network’s vulnerability to cyberattacks, underscoring the need for stringent cybersecurity measures. Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) now prioritize secure connectivity options, leveraging advanced security and networking solutions to protect against potential threats.
In this blog, showcasing the importance of cybersecurity within IIoT environments, outlining the unique challenges posed by embedded systems in industrial settings. It also shades light on proactive strategies to safeguard these systems against evolving cyber threats, ensuring resilience and security in today’s digital manufacturing landscape.
Importance of Cybersecurity in IIoT
Cybersecurity is critically important in Industrial IoT (IIoT) because these systems are responsible for managing essential industrial operations such as manufacturing, energy grids, and transportation. A cyberattack on IIoT systems could result in significant disruptions, leading to operational downtime, financial losses, and potential damage to infrastructure. Additionally, IIoT systems handle sensitive data related to industrial processes, employees, and customers, making data protection a top priority. Ensuring cybersecurity also helps maintain safe working environments, especially in industries where breaches could lead to hazardous conditions for workers and the public. Furthermore, industries are required to comply with stringent cybersecurity regulations, and failing to protect IIoT systems can result in legal consequences and damage to the company's reputation. Therefore, robust cybersecurity is essential not only for protecting critical infrastructure but also for maintaining operational integrity, ensuring compliance, and safeguarding the trust of stakeholders and customers.
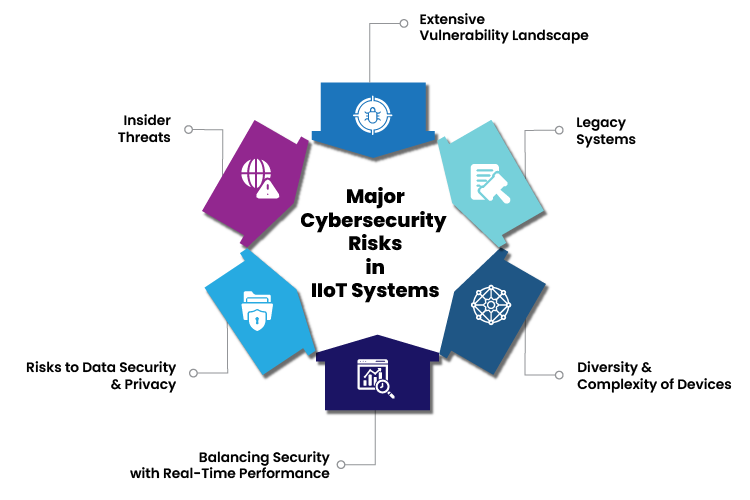
Major Cybersecurity Risks in IIoT Systems
Extensive Vulnerability Landscape
The interconnected nature of IIoT networks, with numerous devices communicating across a system, creates a vast attack surface. Each connected device—whether a sensor, machine, or controller—becomes a potential vulnerability that hackers can exploit. Securing all devices in such a broad and diverse network presents a major challenge.
Legacy Systems
Many industrial systems in use today were designed long before cybersecurity was a key concern. These legacy systems often don’t have modern security features, making them highly vulnerable to attacks. The risk is further increased when these outdated systems are integrated with newer, connected technologies without proper security enhancements.
Diversity & Complexity of Devices
IIoT environments are made up of diverse devices, each with varying levels of security. From simple sensors to complex machines, ensuring uniform security protocols across all these devices is difficult. This inconsistency creates potential weak spots within the system that attackers can target.
Balancing Security with Real-Time Performance
IIoT systems often require real-time data processing and decision-making, especially in environments like manufacturing or logistics. While robust cybersecurity measures are necessary, they must be implemented in a way that does not compromise the real-time performance of the systems, which is critical for operational efficiency.
Risks to Data Security and Privacy
IIoT systems produce vast volumes of sensitive and operational data, making it essential to protect this information from unauthorized access, tampering, or theft. Beyond safeguarding the data, organizations face the added complexity of ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with authorized access to IIoT systems can inadvertently or deliberately create security vulnerabilities. Insider threats are difficult to detect because these individuals typically have legitimate access to critical systems, making it challenging to mitigate the risks they pose.
Solutions to IIoT Cybersecurity Challenges
Holistic Security Approach
Establishing a tailored security framework specifically for IIoT environments is crucial. This framework should encompass policies, procedures, and technologies designed to protect the entire IIoT ecosystem. Regular updates and reviews of the framework ensure its effectiveness against evolving cyber threats.
Robust Device Verification
It is essential to ensure that all devices within the IIoT network are both authenticated and authorized. Implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and digital certificates, verifies the identities of devices and users accessing the network, enhancing overall security.
Data Encryption and Integrity
Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest is vital to prevent unauthorized access. Utilizing strong encryption protocols ensures that intercepted data remains unreadable to attackers. Furthermore, secure key management practices are essential for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
Proactive Security Assessments
Conducting frequent security audits is critical for identifying vulnerabilities within the IIoT network. These audits should be complemented by timely software updates and effective patch management to address known security issues. Keeping systems and devices updated is a fundamental practice to mitigate cybersecurity risks.
Strategic Network Isolation
Segmenting IIoT networks into smaller, isolated subnetworks can significantly limit the impact of a potential breach. By containing threats within specific segments, network segmentation prevents the spread of malware or unauthorized access across the entire network. Implementing virtual local area networks (VLANs) and firewalls aids in achieving effective segmentation.
Real-Time Threat Detection
Utilizing advanced monitoring and anomaly detection systems can identify unusual behavior within the IIoT network. Leveraging machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) enables real-time analysis of patterns, facilitating swift responses to potential threats.
Cybersecurity Education for Staff
Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices is vital for mitigating insider risks. Regular training sessions, awareness programs, and simulated phishing exercises empower employees to recognize and effectively respond to cybersecurity threats.
Collaborative Defense Strategies
Engaging in collaboration with industry peers, cybersecurity experts, and government agencies can significantly enhance an organization’s cybersecurity posture. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices ensures that organizations remain informed about emerging threats and effective mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
The convergence of IoT with industrial operations (IIoT) brings remarkable opportunities for automation, operational insights, and efficiency. However, as this network of connected devices expands, so does the risk of cyber threats. Addressing cybersecurity in Industrial IoT is no longer optional but a critical business imperative. From safeguarding sensitive data to maintaining operational continuity, the right cybersecurity practices protect both the technological infrastructure and the trust of clients, employees, and partners. By implementing robust device authentication, network segmentation, data encryption, and continuous monitoring, industries can mitigate many cybersecurity challenges. Moreover, fostering a security-conscious culture through staff training and collaboration across sectors enhances an organization’s resilience. For the sustainable and secure growth of IIoT, industries must stay agile, prioritizing an integrated approach to cybersecurity that evolves with emerging technologies and threats.
For the latest updates or additional information, feel free to contact ACL Digital.