Sagar Nangare
Service Orchestration: The Key to Building a Future-Proof 5G RAN
We understand that 5G and future-generation networks are built upon a service-based architecture, representing a significant departure from the network structures of previous generations. As we transition to autonomous iterations of 5G networks, they are becoming increasingly populated with a wide range of services, extending from the central telecommunications cloud to the network’s edges. Services are at the essence of 5G networks, and their primary purpose is facilitating the provision of new use cases for end-users.
5G is about providing such services to either end users any consuming devices. Here is one example:
A company wants to deploy a new 5G service for autonomous driving. The service requires a dedicated network slice with high reliability and low latency. Service orchestration can be used to automate the creation and management of the network slice, ensuring that it meets the specific needs of the autonomous driving service.
The service orchestration system must first identify the resources required for the network slice. It would include radio spectrum, network bandwidth, and computing resources. The system would then need to allocate these resources to the network slice and configure them to meet the required performance guarantees.
The service orchestration system must monitor the network slice to ensure that it performs as expected. If there are any problems, the system must take corrective action to restore the network slice to its normal operating state.
Increasingly crucial will be the use of service orchestration to deploy and manage 5G services as 5G networks become more complex and heterogeneous, ensuring the efficient and reliable delivery of services. It serves as just one example.
RAN Orchestration
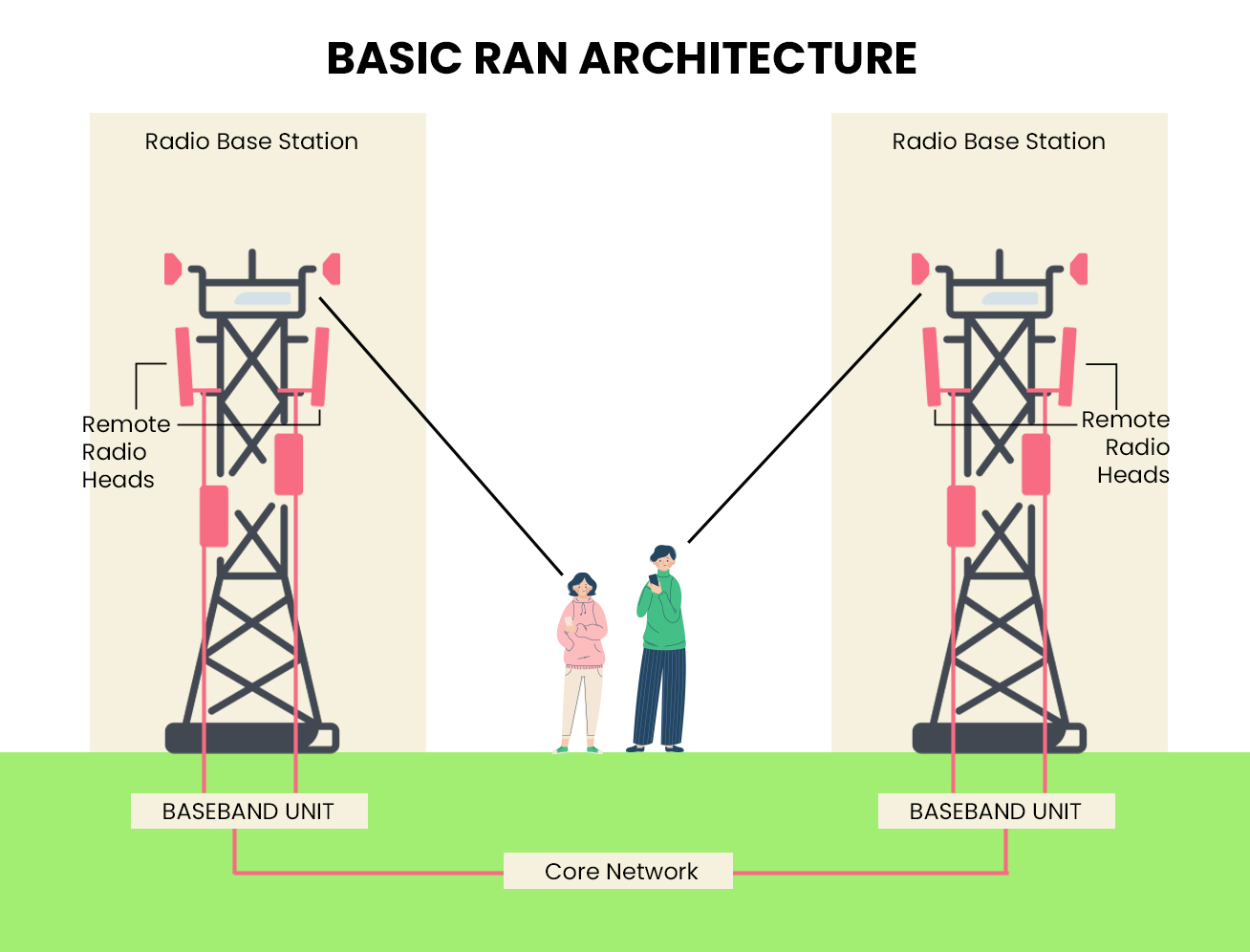
The RAN is the part of a mobile network that connects end-user devices, such as smartphones, to the core network infrastructure. It includes all the base stations, antennas, and associated equipment facilitating wireless communication.
In the world of 5G, where the demands for speed, low latency, and flexibility are more significant than ever, Radio Access Network (RAN) orchestration is not a luxury but a necessity. It enables network operators to harness the full potential of 5G technology by automating complex tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring the delivery of diverse services with stringent quality requirements. As 5G continues to evolve, RAN orchestration will remain a fundamental pillar in building and managing future networks. It is the key to unlocking the true potential of 5G and delivering on its promises of ultra-fast, reliable, and responsive connectivity.
Key Use Cases for Service Orchestration in 5G RAN
Service orchestration in the context of 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) plays a crucial role in optimizing network performance, managing resources efficiently, and delivering various services to end-users. Here are some key use cases for service orchestration in 5G RAN:
Network Slicing
Service orchestration enables the creation and management of network slices, which are isolated virtual networks tailored for specific use cases (e.g., IoT, augmented reality, autonomous vehicles). Orchestration ensures that resources are allocated appropriately to each slice to meet requirements.
Resource Allocation
Service orchestration helps dynamically allocate resources such as spectrum, bandwidth, and computing power based on the current network conditions and service demands. It ensures optimal resource utilization and minimizes latency.
Load Balancing
Orchestration can balance the traffic load across different RAN cells and base stations to prevent congestion and maintain a high-quality user experience.
Interference Management
5G RANs can experience interference in dense urban areas. Orchestration can optimize the allocation of resources to mitigate interference and maintain high data rates and low latency.
Mobility Management
5G networks support high-mobility scenarios like connected vehicles and fast-moving trains. Orchestration plays a role in managing handovers and ensuring uninterrupted connectivity as users move between cells.
Energy Efficiency
Orchestration can optimize the power consumption of RAN equipment by dynamically adjusting transmit power and putting cells into sleep mode when traffic is low, thus reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
Service Assurance
Orchestration tools can monitor network performance in real time and take corrective actions when issues arise, ensuring high service quality and availability.
Network Synchronization
For services requiring tight synchronization, such as 5G low-latency applications, orchestration can ensure that the necessary synchronization mechanisms are in place across the RAN.
Security
Orchestration can enforce security policies and protocols to protect the 5G RAN from various threats, including unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
Service Lifecycle Management
Orchestration assists in the end-to-end lifecycle management of services, from provisioning to scaling and decommissioning, making it easier for network operators to introduce new services and adapt to changing demands.
Quality of Service (QoS) Management
Orchestration can prioritize traffic and allocate resources to ensure that critical services receive the required QoS levels, meeting the diverse needs of different applications and users.
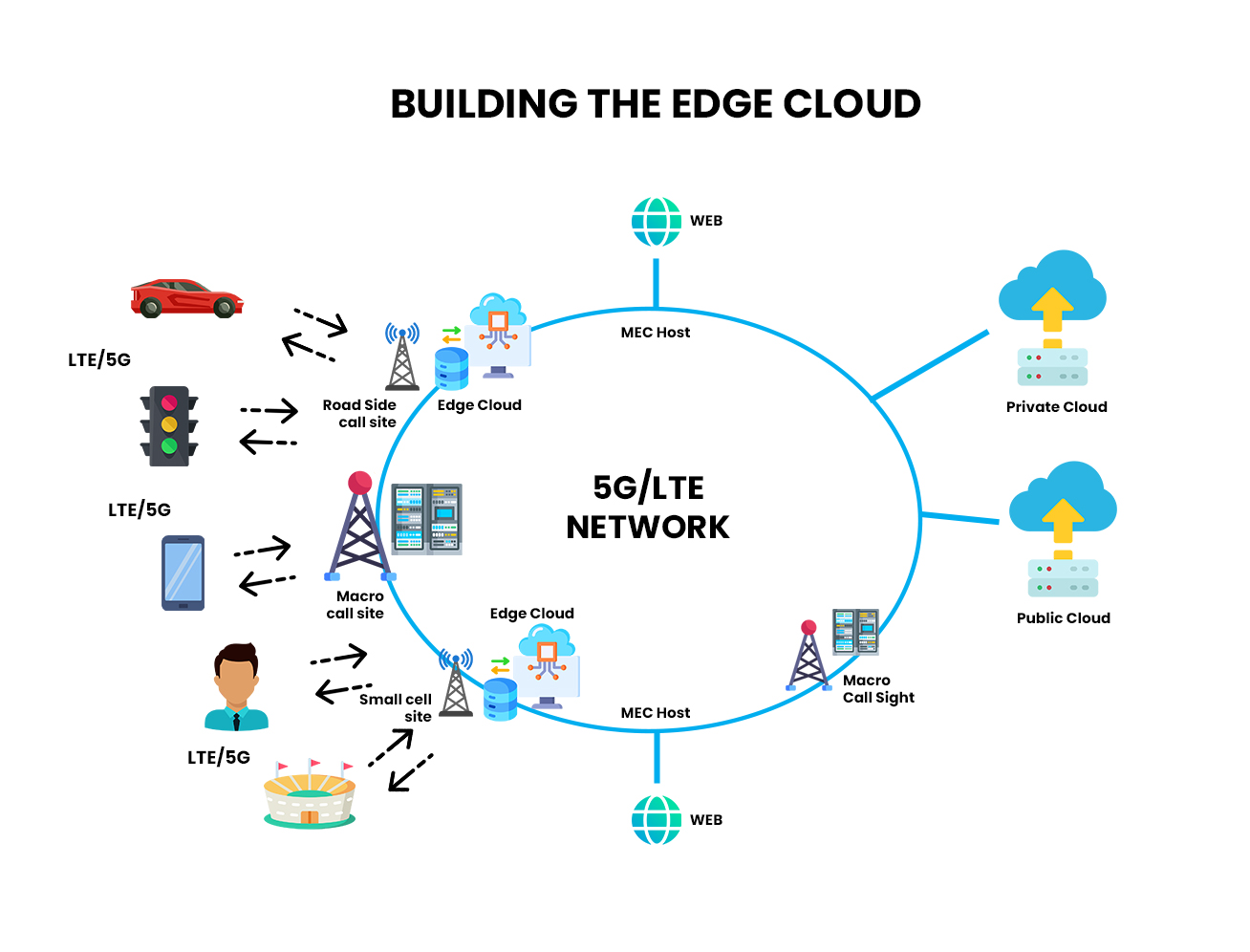
Edge Computing Integration
As 5G networks enable edge computing capabilities, orchestration can manage the deployment and scaling of edge resources at the RAN edge to support low-latency applications and services.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) Integration
Orchestration can deploy and manage virtualized network functions (VNFs) at the RAN, enabling flexible and cost-effective network architecture.
These use cases highlight the critical role of service orchestration in optimizing 5G RAN performance, ensuring efficient resource utilization, and enabling a wide range of innovative services across various industries. Service orchestration helps network operators adapt to the dynamic nature of 5G networks and deliver superior experiences to users and businesses.
Conclusion
Service orchestration is essential for building a future-proof 5G RAN. It enables network operators to automate and simplify the deployment, management, and operation of complex 5G networks. Service orchestration also helps to improve network performance, reliability, and security.
Related Insights

Semiconductors Leading the Charge in the Transition to 6G and Future Tech

Optimizing the Flow: How Software Manages Fiber Optic Networks

Protecting User Data in an Evolving Digital Landscape

Advancements in GenAI for Enhanced O&M and Computing Optimization