

Neet Bhagat
Real-time Analytics and Interoperability in Wearable Health Technology: Revolutionizing Patient Care
Wearable health technology has revolutionized how we monitor and manage our health by enabling real-time data processing and analytics. These devices provide instant insights and recommendations that significantly enhance patient care and wellness. Additionally, the integration and interoperability of wearable devices with healthcare systems are crucial for creating a connected and efficient healthcare ecosystem. This blog explores the transformative impact of real-time analytics and interoperability in wearable health technology, highlighting their benefits, applications, and the challenges involved.
Real-time Analytics in Wearables
Wearable health technology has brought about a revolution in how we monitor and manage our health. One of the critical capabilities driving this change is the real-time data processing and analytics performed by these devices. The ability to quickly and efficiently analyze health data as it is collected can provide instant insights and recommendations that significantly improve patient care and wellness.
Data Collection and Transmission
Wearable devices are equipped with various sensors that continuously collect health data such as heart rate, physical activity, sleep patterns, and more. This data is then transmitted wirelessly to connected devices like smartphones or tablets, and from there, it is uploaded to cloud-based servers for further processing.
- Sensors and Detection: Modern wearables include advanced sensors that can detect even minor changes in physiological data, ensuring a high degree of accuracy.
- Wireless Transmission: Data is transmitted in real-time using technologies such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, ensuring that users and healthcare providers have up-to-date information.
- Cloud Upload: Once the data reaches a connected device, it is securely uploaded to cloud servers where it can be stored and analyzed.
Real-time Processing and Analysis
Once the data is in the cloud, it undergoes real-time processing and analysis. This involves filtering the data, identifying significant patterns, and generating actionable insights.
- Data Filtering: Raw data is cleaned to remove noise and irrelevant information. This step ensures that only useful data is analyzed.
- Pattern Recognition: Advanced algorithms, often powered by AI and machine learning, identify patterns and anomalies in the data. For example, a sudden increase in heart rate during rest might be flagged for further investigation.
- Actionable Insights: The processed data is translated into actionable insights, such as alerts for irregular heart rhythms or recommendations for increased activity.
Benefits of Real-time Analytics
The ability to process and analyze data in real-time offers several significant benefits for patient engagement and wellness.
- Immediate Health Feedback: Users receive instant feedback on their health metrics, allowing them to make timely adjustments to their lifestyle or seek medical advice when necessary.
- Proactive Health Management: Continuous monitoring helps in early detection of potential health issues, leading to proactive management and preventive care.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: When patients have access to real-time health data, they become more engaged in their health journey, making informed decisions about their well-being.
Real-world Applications
Real-time data processing and analytics in wearable health technology have found numerous applications in the medical field, ranging from everyday fitness tracking to managing chronic diseases.
- Chronic Disease Management: Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) for diabetics and wearable ECG monitors for heart patients are prime examples of how real-time data can be crucial in managing chronic conditions.
- Fitness and Wellness: Wearables like Fitbit and Apple Watch help users manage their fitness goals by providing real-time feedback on physical activities, sleep, and nutrition.
In summary, real-time data processing and analytics are foundational to the impact of wearable health technology on patient engagement and wellness. By providing instant feedback, enabling proactive health management, and enhancing patient engagement, these capabilities are changing the face of healthcare.
Integration and Interoperability
Wearable technology stands out as an essential innovation. These devices, ranging from fitness trackers to medical-grade monitors, offer immense potential for improving patient care. However, their true value emerges when they can seamlessly connect and communicate with broader healthcare systems. This is where the concepts of integration and interoperability become essential. These two aspects ensure that data collected by wearables can be efficiently used by healthcare providers, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Understanding Integration in Wearable Health Technology
Integration in the context of wearable health technology refers to the seamless connection of wearable devices with other healthcare systems. It involves the merging of different technologies so that they work together within a single framework. This process allows data from wearables to be transferred, stored, and analyzed in conjunction with other medical data.
Types of Integration
- Device-to-Device Integration: This type involves direct communication between two or more wearable devices. For example, a fitness tracker might send heart rate data to a smartwatch for further analysis.
- Device-to-Cloud Integration: Data from the wearable is sent to a cloud server where it can be accessed and analyzed by healthcare providers or applications. This method is common in telemedicine.
- Device-to-EHR Integration: Wearable devices connect directly with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, enabling real-time updates to a patient’s medical record. This integration supports better monitoring and personalized care.
The Importance & Benefits of Integration
Integration refers to the ability of wearable devices to connect and share data seamlessly with healthcare systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR). This is essential for several reasons:
- Comprehensive Health Monitoring: By integrating data from multiple sources, healthcare providers get a complete view of a patient’s health. This enables better diagnostics, treatment plans, and monitoring of chronic conditions.
- Real-Time Data Access: Integrated systems allow real-time access to health metrics, facilitating timely interventions. For example, if a wearable detects an abnormal heart rate, a notification can be sent directly to a healthcare provider.
- Personalized Care: Integration supports personalized healthcare by providing detailed insights into a patient’s daily habits and health trends. This data can be used to tailor treatment plans and lifestyle recommendations.
- Operational Efficiency: Integrated systems streamline workflows by reducing manual data entry and minimizing errors, making healthcare delivery more efficient.
Interoperability in Wearable Health Technology
Interoperability means different health technology platforms can talk to each other and share data effectively. For wearable health devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical sensors, this is crucial. It ensures that data collected by these devices can be easily integrated with other systems, including mobile health apps, electronic health records (EHRs), and larger healthcare IT infrastructures. Imagine your fitness tracker syncing effortlessly with your doctor’s EHR system, giving your healthcare provider a complete picture of your health. That’s the power of interoperability.
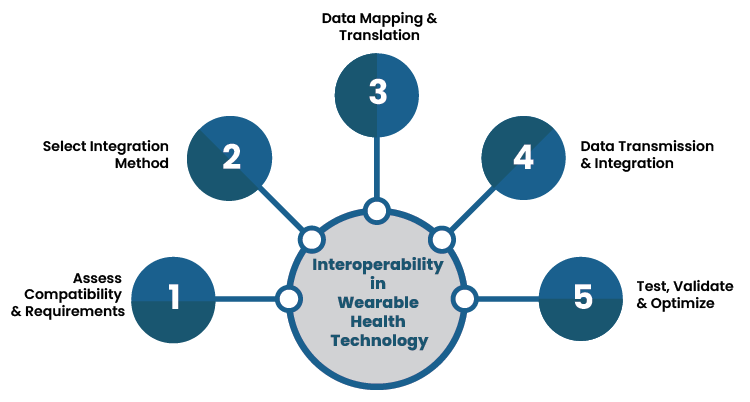
Strategies of Enhancing Interoperability
Strategies to enhance interoperability involve developing frameworks and adopting technologies that promote seamless communication between devices and systems:
- Use of APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) facilitate data exchange by allowing different systems to communicate with each other. APIs can standardize interactions, making it easier to integrate various health technologies.
- Adopting HL7 and FHIR Standards: Health Level Seven (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) are standards designed to improve the exchange of electronic health information. Adopting these can enhance interoperability significantly.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance data security and interoperability by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof way to manage health records. This ensures data integrity and accessibility while preserving patient privacy.
Challenges in Achieving Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different wearable devices and healthcare systems to work together, exchange information, and interpret shared data. Achieving this presents several challenges:
- Standardization: Different manufacturers use various data formats, making it difficult to standardize and share information between devices and systems. Establishing common standards is crucial for seamless data exchange.
- Data Quality and Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of data from multiple sources can be challenging. Discrepancies in data can lead to incorrect diagnoses or treatment plans.
- Privacy and Security: Integrating and sharing health data raises concerns about privacy and security. Robust encryption and secure data management practices are essential to protect sensitive information.
Real-World Applications
Integration and interoperability are already making significant impacts in healthcare:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Integrated wearables enable healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enabling timely interventions.
- Telemedicine: Wearables integrated with telemedicine platforms enhance the quality of remote consultations by providing real-time health data, making virtual appointments more effective.
- Chronic Disease Management: Continuous integration of data from wearables helps in the effective management of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension. For instance, integrated glucose monitors provide real-time blood sugar levels, aiding in better diabetes management.
- Emergency Response: Wearables can detect emergencies and automatically alert healthcare providers or emergency contacts, ensuring timely interventions. For example, a smartwatch detects an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia) and sends an alert to the patient’s cardiologist. The doctor can review the data in real-time and decide whether the patient needs to come in for an urgent evaluation or if an emergency response is necessary.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Data from wearables can help tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on real-time health metrics, enhancing the precision of medical care. A patient recovering from surgery, for example, wears a smartwatch that tracks their activity levels and vital signs. The healthcare team uses this data to create a personalized rehabilitation program that adjusts based on the patient’s progress and activity levels.
While integration and interoperability of wearable health technology come with challenges, they are critical for providing comprehensive, real-time, and personalized healthcare. These advancements promise a more connected and efficient healthcare system, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
ACL Digital offers robust capabilities in providing real-time analytics and interoperability within the wearable health technology sector. Integration and interoperability of wearable health technology, though challenging, are essential for delivering comprehensive, real-time, and personalized healthcare solutions. These advancements enable a more connected and efficient healthcare system, significantly enhancing patient outcomes by providing timely and accurate health data for better decision-making and patient care. Get in touch with the experts at business@acldigital.com for more details.
Related Insights


Why Network Transformation?

Cloud Computing Simplified

How to Choose a Product Engineering Vendor?

5 Futuristic Game Changing Technologies Transforming Retail

