Benny Ruban
Navigating the Landscape of Desktop as a Service (DaaS): Challenges and Considerations
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) represents a paradigm shift in cloud computing, a cutting-edge solution, fundamentally transforming how organizations approach desktop infrastructure. In essence, DaaS migrates the traditional desktop environment to the cloud, offering users access to virtualized desktops from any internet-connected device. Let’s delve deeper into the transformative potential of DaaS and its multifaceted advantages.
Cloud-Based Delivery
Desktop computing services delivered over the internet revolutionize the traditional model by hosting the entire desktop environment, including the operating system, applications, and data in the cloud. Users access their virtual desktops remotely from any internet-connected device, flexibility and enabling remote work. This cloud-based delivery model operates on a subscription basis, offering scalability, centralized management, and enhanced security measures. With DaaS, organizations experience cost savings, resource efficiency, and seamless integration with other cloud services, ushering in a new era of accessible and agile desktop computing.
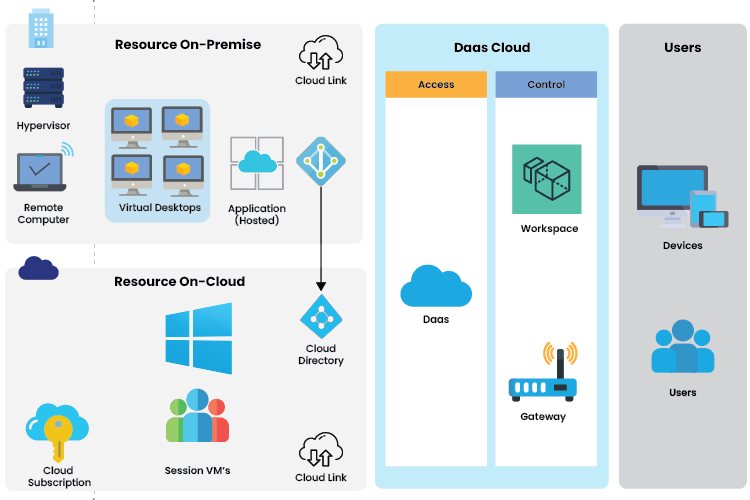
DaaS Architecture
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) providers offer flexible deployment options, including hybrid or fully cloud-based solutions. In a hybrid setup, virtual appliances maintained on-premises connect to cloud resources, often powered by Active Directory (AD). A secure cloud link facilitates this connectivity. DaaS providers manage resources and control access, ensuring secure connections for users, whether accessing internally or externally, through secured access gateways.
Security in DaaS Environments
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) security relies on proper measures. Factors affecting security include implementation, provider reputation, and organizational actions. Security considerations for DaaS include:
Provider Security
Opt for reputable providers prioritizing security.
Network Security
Employ firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems for traffic monitoring and control.
Endpoint Security
Implement protection measures on user devices against malware and viruses.
Audits and Monitoring
Conduct regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing.
Data Segmentation
Utilize network segmentation and role-based access controls to isolate sensitive data.
Compliance Measures
Ensure compliance with relevant data protection and privacy regulations based on geographic locations.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing performance in DaaS environments is critical for delivering smooth and responsive user experiences. Key strategies include:
- Efficient Resource Allocation
- Network Optimization to reduce latency
- High-performance Storage Solutions
- Load Balancing for even user connections
- Application and Desktop Image Optimization
- Proactive Monitoring and Analytics
- Effective User Profile Management
- Endpoint Optimization
- Security Measures without compromising performance
User Experience and Personalization in DaaS
Prioritizing a consistent and responsive interface across devices, optimizing for different screen sizes and resolutions, and implementing user profile management for personalized settings are essential for enhancing user experience in DaaS environments. Personalization features such as customization of desktop elements and easy access to personalized applications and data further enrich the user experience, promoting productivity and collaboration.
Cost and Scalability
DaS’s subscription-based model reduces upfront capital costs and offers flexibility to scale up or down based on organizational needs. By eliminating on-premises infrastructure expenses and leveraging shared infrastructure for cost savings, DaaS optimizes total cost of ownership (TCO) and allows organizations to focus on core business activities while benefiting from rapid deployment capabilities and economies of scale.
DaaS for Remote Work
DaaS offers numerous advantages for remote work scenarios. It enables users to access their desktop environments from anywhere with an internet connection, providing a seamless and flexible work experience. DaaS is device-agnostic, allowing users to work on various devices, promoting flexibility and adaptability.
Security is enhanced through centralized measures, ensuring data protection and aiding organizations in maintaining compliance standards. The scalability of DaaS allows organizations to easily adjust their virtual desktop infrastructure to accommodate the changing needs of a remote workforce, and its cost-efficient subscription-based model reduces upfront capital expenses. With rapid deployment capabilities, and consistent user experience, DaaS is a valuable solution for optimizing productivity and collaboration in remote work settings.
Disaster Recovery
Centralization
Data and desktops are centralized in the cloud for streamlined recovery processes.
Redundancy
Providers ensure redundancy and backups to enhance data resilience.
Business Continuity
Enables uninterrupted business operations by granting access to virtual desktops during disruptions.
Quick Restoration
Facilitates swift restoration of desktop services, reducing downtime.
Flexible Access
Users can access desktops from diverse devices, supporting remote work continuity during disasters.
Device Independence in BYOD
DaaS accommodates Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, allowing users to securely access virtual desktops and applications from personal devices. This enhances mobility and flexibility in the work environment while maintaining robust security measures to ensure a secure work environment.
Disadvantages of DaaS
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) presents its own set of challenges. Relying on internet conectivity may result in accessibility and performance issues, and some DaaS solutions offer limited customization compared to on-premises setups. Security concerns emerge with data stored in the cloud, necessitating robust measures. While embracing an operational expenditure (OpEx) model, long-term subscription costs can accumulate. Performance fluctuations may occur due to varying internet connection quality and server resources, while compliance issues may arise from data sovereignty regulations. Transitioning from existing systems poses its own hurdles, and organizations may become reliant on the DaaS provider’s infrastructure and service quality, introducing vendor dependence. Therefore, careful consideration of these drawbacks is imperative when contemplating DaaS adoption.
Conclusion
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) offers a comprehensive solution for delivering virtual desktop environments to users. Its key benefits include flexibility, scalability, centralized management, security, performance optimization, cost efficiency, and enhanced productivity. By leveraging DaaS, organizations can modernize their desktop infrastructure, support remote work, and drive digital transformation initiatives effectively.
Related Insights
Why 2026 Will Be a Breakthrough Year for AI Chips and Semiconductors