

ACL Digital
The Role of NB-IoT in Advancing the Internet of Things
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize businesses, new technologies are emerging to address specific use cases. IoT, a groundbreaking concept that connects physical objects to the Internet, offers endless possibilities—from automating utility meter readings for homeowners to enabling smoke detectors to alert local fire departments. However, the rapid increase in connected devices poses a significant challenge for mobile network operators: managing the sheer volume of devices on their networks. Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) provides a solution. NB-IoT is a low power wide area network (LPWAN) technology designed to support a broad range of IoT applications. This article explores how NB-IoT works, its benefits, applications, and the barriers to its adoption, while also comparing it with other IoT technologies.
How Narrowband IoT Works?
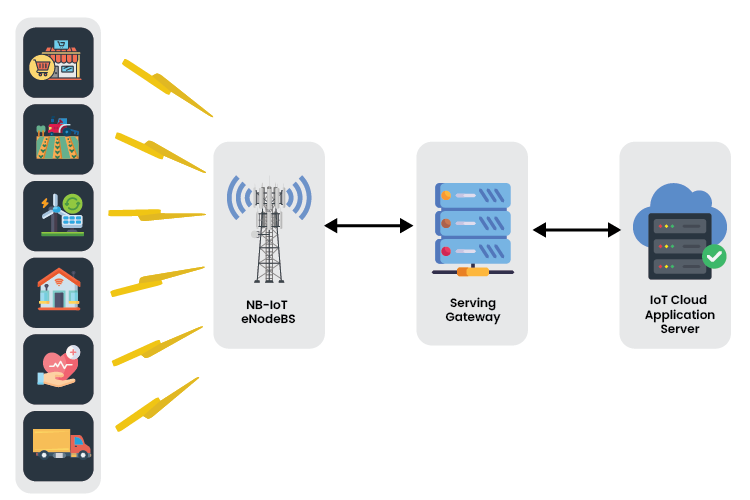
- NarrowBand IoT (NB-IoT) operates through specially designed devices and sensors that are the fundamental components of NB-IoT systems.
- These devices gather information from their surroundings and transmit it to NB-IoT base stations or transmission nodes.
- Each base station is connected to an IoT gateway and IoT cloud application servers, enabling centralized monitoring and data analysis.
- Sophisticated analysis tools facilitate real-time monitoring of complex networks.
- Customized mobile applications enhance user convenience for real-time monitoring and data management.
- This seamless integration allows for efficient data collection, transmission, and analysis, making NB-IoT an effective solution for various IoT applications.
Why Use NarrowBand IoT?
NarrowBand IoT offers several benefits for IoT applications. Here are a few major reasons to use it.
Extended Coverage
NB-IoT provides extensive coverage, reaching areas where traditional cellular networks may struggle. It offers improved indoor and underground penetration, making it suitable for use cases like smart meters in basements or agricultural sensors in rural areas.
Low Power Consumption
One of the significant advantages of NB-IoT is its low power consumption, which extends the battery life of IoT devices. This feature is crucial for applications like environmental monitoring and smart cities, where devices are often deployed in hard-to-reach areas and expected to operate for years without frequent battery replacements.
Cost-Effective Connectivity
NB-IoT modules are generally more cost-effective compared to other cellular modules. The simplicity of the NB-IoT protocol stack reduces the complexity and cost of the hardware, making it an affordable option for large-scale IoT deployments.
High Connection Density
NB-IoT can support a large number of devices within a small geographical area, making it perfect for urban environments and smart city applications where numerous sensors and devices need simultaneous connectivity. Additionally, NB-IoT signals can travel long distances, enabling connectivity in remote areas. Its use of cellular technology ensures both reliability and security.
Enhanced Security
NB-IoT leverages the security features of LTE networks, providing robust encryption and secure data transmission. This level of security is essential for applications that handle sensitive data, such as healthcare and smart home devices.
NarrowBand IoT Versus Other Technologies
Here’s a comparison chart outlining the main similarities and differences between SIGFOX, LoRa (Long Range Radio), LTE-M (Long Term Evolution – Machine Type Communication), and NarrowBand IoT (NB-IoT):
| Basis | LoRa | SIGFOX | LTE-M | NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage/Range | 10Km approx | 12Km approx | 11Km approx | 15Km approx |
| Data Rate | 10Kbps | nearly 100 bps | nearly 10Mbps | 100Kbps |
| Spectrum | Unlicensed | Unlicensed | Licensed | Licensed |
| Maximum Number of messages/day | 50000(BTS) | 140 devices | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Power Consumption | Low-Medium | Low | Low | Low |
NarrowBand IoT Applications and Use Cases
NB-IoT is well-suited for various IoT applications across multiple domains. Here, we explore its primary areas and examples of use.
Smart Cities
Modern cities leverage smart technology to mitigate emissions, enhance air quality, and optimize connectivity and mobility services for residents. NB-IoT plays a pivotal role by supporting diverse applications such as smart building systems, city lighting,thereby enhancing overall safety and efficiency for citizens.
Retail
NB-IoT enhances logistics operations through real-time asset tracking, temperature monitoring of sensitive goods, and rapid reporting capabilities, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Agriculture
NB-IoT sensors in fields monitor soil conditions, humidity, and crop health, enabling data-driven decisions on irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. In livestock management, NB-IoT devices track and monitor livestock activities, providing real-time data on location, health status, and behavior for improved husbandry practices.
Energy
NB-IoT technology enables precise, real-time smart metering for energy, water, and gas usage, enhancing resource efficiency. It empowers consumers and utilities to optimize consumption patterns. NB-IoT also strengthens grid monitoring, ensuring reliable energy distribution by detecting issues promptly. This demonstrates its crucial role in advancing sustainability and energy management across sectors.
Smart Homes
NB-IoT can be integrated into home ecosystems for home automation solutions like thermostats,and door locks, providing homeowners with enhanced control and security. Additionally, NB-IoT technology can be utilized in wearable devices for health and fitness monitoring, delivering valuable data to individuals and healthcare professionals.
Healthcare
NB-IoT technology enables continuous remote monitoring of patients’ health conditions through devices like heart and blood pressure monitors, ensuring timely medical intervention and reducing hospital visits. Hospitals use NB-IoT to track the location and status of medical equipment in real-time, optimizing resource allocation and enhancing operational efficiency.
Transportation
NB-IoT networks enable smart parking solutions, allowing drivers to locate available parking spaces in real-time, reducing congestion and enhancing urban mobility. NB-IoT facilitates the management of electric vehicle charging stations, ensuring availability and efficient utilization of charging facilities.
Automotive
NB-IoT supports the integration of advanced features in connected vehicles such astelematics for tracking vehicle performance, and diagnostics systems for proactive maintenance.
Barriers to NarrowBand IoT
NB-IoT is a technology that has just been introduced. Following are some barriers to its adoption:
- Fewer NB-IoT devices and modules available compared to other IoT technologies, largely because NB-IOT is in its early stage of adoption.
- NB-IoT modules may have a higher initial cost than other IoT technologies, which could discourage some businesses from adopting.
- NB-IoT’s data transfer speeds are lower than those of LTE Cat-M1, which may not be suitable for applications that require higher data throughput.
- The design of NB-IoT is to be used with devices that are often inactive or inconsistently transmitting data, which limits its use in more real time applications.
- NB-IoT is unsuitable for voice calls due to the absence of Voice over LTE (VoLTE) support.
- The deployment and wider adoption of NB-IoT may face challenges if carriers opt for LTE support.
NarrowBand IoT (NB-IoT) stands out as a promising technology for various IoT applications, offering extensive coverage, low power consumption, and cost-effective connectivity. It is particularly effective in scenarios requiring long battery life and reliable performance in challenging environments. However, despite its advantages, NB-IoT faces barriers such as limited device availability, higher initial costs, and lower data transfer speeds. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and developers looking to adopt NB-IoT. By comparing NB-IoT with other technologies, stakeholders can make informed decisions about the best IoT solutions for their specific needs.
Get to know our success stories and feel free to contact ACL Digital.
Related Insights


