

Naresh Kumar B
Invisible Phishing Attack
Invisible phishing attack is a form of fraud in which the attacker tries to learn information such as login credentials or account information by masquerading as a reputable entity or person in email, IM or other communication channels.
An Information Security researcher from China has reported about a phishing attack, which is almost impossible to detect. Most careful users on the internet are also tricked by Hackers.
The web browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome has some known vulnerabilities, which is used by hackers to display their own domain name (fake) as the sites of legitimate services (Apple, Google, or Amazon) to sneak login or financial credentials and other sensitive information from users.
As a defence mechanism against Phishing attack, verifying the address bar after the page has loaded and if it is being served over a valid HTTPS connection. The legitimate site address of Apple (https://www.apple.com) in the address bar secured with SSL, but the content on the page is coming from another server, then your browser is vulnerable. The principle behind such attack is called as homograph attack. Please refer below screenshot.
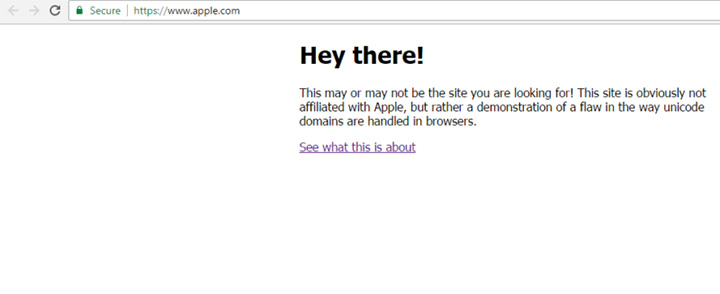
What is homograph attack?
This attack is like a spoofing attack, where the address of a website looks legitimate but the characters of the site name have been replaced deceptively with Unicode characters. Usually Unicode characters, represent alphabets like Greek, Cyrillic, and Armenian in internationalised domain names, look the same as Latin letters to the casual eye but are treated differently by computers with the completely different web address.
Below URLs may fool some less experienced users:
http://www.g00gle.co.in
http://bl00mberg.com
Punycode Phishing Attacks
Many web browsers use ‘Punycode’ encoding by default to represent Unicode characters in the URL to defend against Homograph phishing attacks. A special encoding technique is called Punycode which is used in the web browser to convert Unicode characters to the limited character set of ASCII (A-Z, 0-9), supported by International Domain Names (IDNs) system.
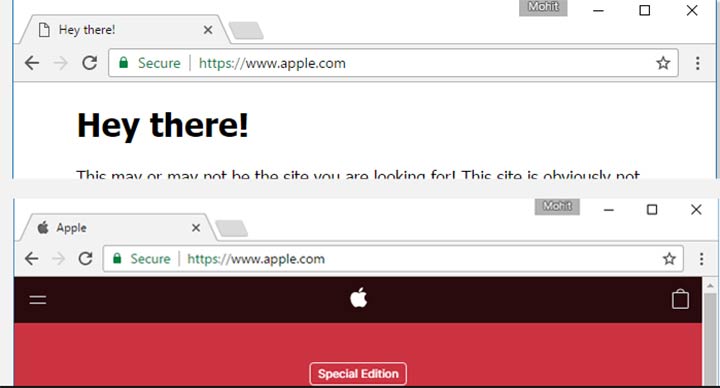
A random test was done by a researcher from china by registering a domain name xn--80ak6aa92e.com and he bypassed the protection, which appears as “apple.com” by most vulnerable web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera. The xn-- prefix is known as an ‘ASCII compatible encoding’ prefix, which indicates web browser that the domain uses ‘punycode’ encoding to represent Unicode characters, and because the researcher used the Cyrillic “а” (U+0430) rather than the ASCII “a” (U+0041), the defence approach implemented by web browser failed.
How to prevent against Invisible Phishing attacks?
Be sceptical of emails indicating that you must make changes to your accounts, or warning stating that your account will be terminated if you do not perform some online activity.
Review the address bar (of the browser) to see if the domain name is correct.
When submitting any type of financial document or credentials, check for secure connection , which is indicated in the address bar (https://) and a closed – padlock icon in the browser.
Do not click the HTML link within the email. Type the URL out manually.
Do not accept email in HTML format
Related Insights

