
ACL Digital
5 Minutes read
Transform Your Home with Smart Energy Management
A Home Energy Management System, or HEMS, is a digital system that monitors and controls energy generation, storage and consumption within a household. HEMS usually optimizes for a goal such as cost reduction, self-sufficiency maximization or emissions minimization. With the increasing adoption of electric mobility and heating, residential PV, and dynamic tariffs HEMS are becoming more popular as the saving potential increases. The market for home energy management systems was valued at USD 3.64 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a 13.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 2023 and 2030.
Key Technical Requirements for Implementing a Home Energy Management System (HEMS)
To ensure a seamless and efficient Home Energy Management System (HEMS), certain technical prerequisites must be met. These requirements help maintain stable communication, optimize energy usage, and enable smooth integration of distributed energy resources (DERs).
Reliable Connectivity for Communication
- A stable internet connection ensures seamless communication between the energy management system (EMS), server, and energy devices.
- While an internet connection is beneficial, a local network can also support communication within the household.
Local Gateway for Energy Optimization
- A central control unit, such as a gridBox, serves as the local gateway for optimizing energy flows.
- While cloud-based energy management is an alternative, it introduces higher latency and is less common than local control.
Compatible Software and Applications
- The EMS must integrate with compatible software and mobile applications that allow users to monitor, control, and manage their DERs effectively.
- This software plays a crucial role in real-time tracking, automation, and data-driven decision-making for energy efficiency.
Trends in Residential Energy Storage and Management Systems
Residential Renewable Energy on the Rise
Homeowners are increasingly using renewable energy sources, such as solar electricity, because they are cost-effective. With solar panels and energy storage systems, people can produce and store their own energy. This shift is happening because these systems are now more affordable and accessible. The main challenge, though, is that renewable energy isn’t always available, such as when solar panels can’t generate power at night.
Home Battery Storage Systems (BSS)
In order to counter grid demand and provide resilience during outages, BSS stores extra energy from renewable sources. These systems lower electricity costs, enable selling surplus energy back to the grid, and support a decentralized energy landscape. Rapid improvements in battery storage technology aim to address seasonal energy imbalances.
Smart Home Energy Management Systems (EMS)
A battery storage system stores and releases energy, while an energy management system (EMS) acts as the brain, controlling how, where, and when the energy is used. Often connected to an app, modern EMS solutions integrate with IoT technology, offering real-time insights into energy usage down to individual devices. This data empowers homeowners to make smarter energy decisions, like cutting HVAC use or replacing inefficient appliances, reducing costs, and improving efficiency.
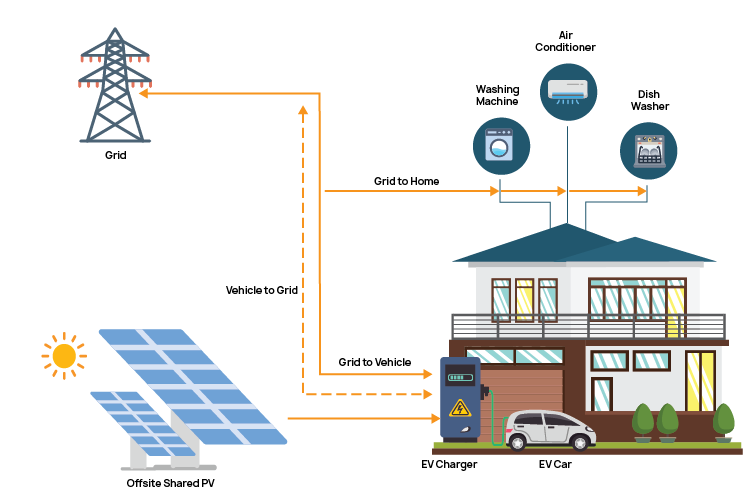
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) Technology
Bidirectional charging systems in EVs like the Ford F-150 Lightning allow vehicles to power homes during outages. Reusing existing EV batteries for residential energy storage is one example of an innovation that increases battery utility and produces sustainable energy solutions. These developments, which combine sustainability, efficiency, and autonomy, demonstrate how home energy is changing.
Use Cases of Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS)
Every household has unique energy needs, and Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) can be customized to fit specific requirements. These systems can range from basic setups with a few assets to more advanced configurations that maximize energy savings.
Real-Time Energy Monitoring
Homeowners may effectively monitor and optimize energy usage with the help of HEMS, which offers real-time data insights on energy consumption, device performance, and overall system health.
Self-Sufficiency Optimization
By prioritizing self-generated renewable energy, HEMS ensures that households consume more of their own power, reducing reliance on the grid, lowering costs, and cutting emissions.
Time-of-Use Tariffs (ToUT) Management
HEMS ensures that homes utilize more of their own electricity by giving self-generated renewable energy priority, which lessens dependency on the grid, lowers expenses, and reduces emissions.
Flexibility Marketing & Grid Interaction
Excess stored energy can be sold back to the grid, allowing homeowners to monetize their energy assets based on electricity price fluctuations and grid demand.
Large-Scale Energy Use Cases
HEMS acts as a foundation for advanced energy models, including:
- Smart Districts: Optimizing energy use across multiple buildings.
- Virtual Power Plants (VPPs): Aggregating energy assets to participate in wholesale energy markets.
- Energy Communities: Enabling peer-to-peer energy trading, where neighbors share surplus power.
The Future of Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS)
The future of Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) is set to be smarter, more sustainable, and highly efficient as emerging technologies transform home energy management.
Increased Integration of Renewable Energy
HEMS will prioritize renewable sources like solar and wind, enabling households to reduce reliance on the grid. Improved battery storage solutions will store excess renewable energy, ensuring availability during peak demand or low generation periods.
Advanced Monitoring with IoT and AI
Future HEMS will leverage smart meters and IoT devices for real-time energy insights, helping homeowners make informed decisions. AI-driven predictive analytics will further optimize storage, forecast energy needs, and enhance overall efficiency.
Smarter Home Automation
Connected smart home appliances, such as thermostats, lighting, and heating systems, will intelligently adapt based on user habits and energy availability. With seamless HEMS integration, smart homes will become more intuitive, energy-efficient, and responsive to real-time energy demands.
Grid-Flexible Homes
Homes will promote grid stability and lower demand during peak hours by both consuming energy and returning excess electricity to the grid. Home-grid interaction will be completely transformed by this move to decentralized energy systems.
Conclusion
Home energy management systems (HEMS) have the potential to completely transform how households produce, store, and use energy in the future. HEMS will improve efficiency, lower costs, and advance sustainability through the smooth integration of sophisticated grid interactions, AI-driven automation, and renewable energy. Homes will become more intelligent, self-sufficient, and able to actively balance energy supply and demand as these systems develop. HEMS will be crucial in forming a more robust and sustainable energy future by promoting decentralized power grids and facilitating increased energy independence.



