

ACL Digital
Generative AI: Leading the Charge in Healthcare Delivery
In today’s healthcare landscape, approximately 5% of patients account for nearly 50% of total healthcare spending, underscoring the urgent need for more efficient and personalized medical solutions. This staggering statistic highlights the immense pressure on the healthcare system to improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficacy, and administrative efficiency. Where the need of generative AI occurs which is a groundbreaking technology poised to revolutionize the medical field.
By leveraging advanced neural networks and machine learning algorithms, generative AI has the potential to transform everything from diagnostics to drug discovery, offering unprecedented opportunities for personalized patient care and operational efficiency. This blog explores how generative AI is set to redefine healthcare, addressing current challenges and paving the way for a future where technology and medicine work hand in hand to enhance patient outcomes and streamline processes.
Introduction to the Technologies behind Generative AI
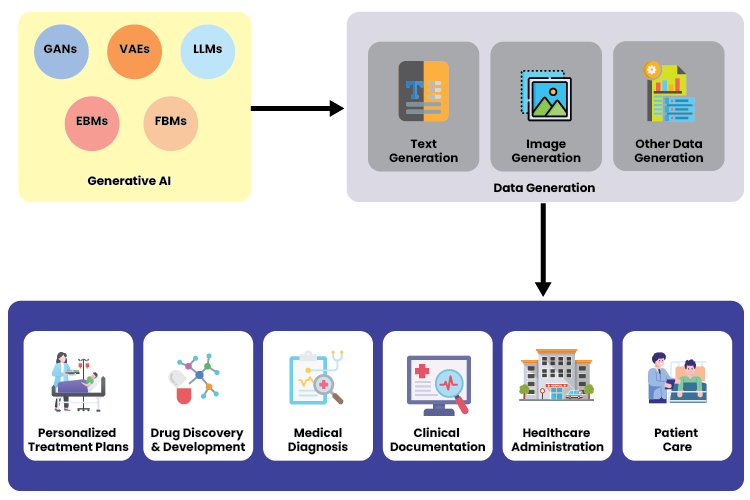
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, images, and even music, by learning from existing data. Unlike traditional AI, which is typically designed to recognize patterns and make predictions based on input data, generative AI goes a step further by producing new, original data that mimics the properties of the training data. This capability stems from its ability to understand and replicate the underlying structures of the data it has been trained on.
At the core of generative AI are several key technologies. Neural networks, particularly deep learning models, are crucial for enabling AI to learn complex patterns from vast amounts of data. Machine learning algorithms allow these models to improve over time through exposure to more data and iterative refinement. Natural language processing (NLP) is another essential component, enabling AI to understand and generate human language with increasing fluency and coherence.
Generative AI is already making significant impacts across various fields. In the creative arts, it is used to generate realistic images, compose music, and write stories. In business, it helps in drafting emails, creating marketing content, and designing products. Healthcare applications include generating synthetic medical data for research, assisting in the creation of personalized treatment plans, and even predicting patient outcomes based on historical data. These examples illustrate the broad potential of generative AI to innovate and enhance numerous domains by creating valuable new data and insights.
How Generative AI is Used in Medical Diagnosis?
Generative AI enhances diagnostic precision by analyzing vast amounts of medical data and identifying patterns that might be imperceptible to human doctors. By learning from a multitude of medical images, patient records, and genetic information, generative AI models can detect subtle indicators of disease at an early stage. This ability to cross-reference and process complex datasets allows AI to provide highly accurate diagnostic suggestions, reducing the likelihood of human error and increasing the chances of early intervention.
“The adoption of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is expected to have a significant economic impact on organizations worldwide as of 2023. The industry anticipating the most significant impact was the high-tech industry, forecasting a minimum increase of approximately 4.8 percent of its global revenue and a maximum increase of 9.3 percent of the industry’s total revenue.” – Statista
Personalized Treatment Plans
Generative AI creates personalized treatment plans by analyzing individual patient data, including medical history, genetic information, lifestyle, and even environmental factors. By leveraging this comprehensive dataset, AI can identify the most effective treatments tailored to each patient’s unique needs. This personalized approach enhances the efficacy of treatments and minimizes potential side effects.
In oncology, AI has been used to tailor chemotherapy treatments to individual patients based on their genetic profiles and the specific characteristics of their tumors. The potential of AI in evolving treatment personalization is huge. Future developments could include real-time treatment adjustments based on continuous patient monitoring, integration of broader datasets (like social determinants of health), and more precise predictive analytics to preemptively address health issues before they manifest.
Drug Discovery and Development
AI fast-tracks drug discovery by quickly analyzing biological data and predicting how different compounds will interact with targets in the body. This significantly shortens the initial stages of drug development, which traditionally take years.
By automating data analysis and predictive modeling, AI reduces the financial burden of drug development. It cuts down the time and resources needed for research, thus lowering overall costs. AI has also played a critical role in developing new drugs, such as identifying potential COVID-19 treatments during the pandemic. AI algorithms sifted through existing drugs and compounds to predict which might be effective against the virus, speeding up the process of bringing treatments to clinical trials.
Enhanced Patient Care
AI-driven virtual health assistants provide round-the-clock support to patients, answering questions, offering medical advice, and reminding patients to take medications. These assistants use natural language processing to understand and respond to patient queries effectively.
AI is used in remote patient monitoring systems to track critical signs, activity levels, and other health metrics. These systems can alert healthcare providers to potential issues in real time, allowing for timely interventions.
AI also improves healthcare accessibility by enabling remote consultations and diagnostics, particularly benefiting remote and underserved populations. Telehealth services powered by AI can provide medical advice and diagnoses without requiring patients to travel to healthcare facilities.
Administrative Efficiency
Generative AI optimizes administrative tasks by automating scheduling, billing, and documentation processes. This reduces the workload on administrative staff and minimizes errors. It also minimizes human errors in administrative functions by ensuring accurate data entry, coding, and billing. This leads to more efficient operations and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
The benefits for healthcare providers and support staff include reduced administrative burdens, allowing them to focus more on patient care. AI also aids in decision-making processes by providing comprehensive data analysis and insights, improving overall healthcare delivery.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges of Generative AI
The ethical considerations and challenges of generative AI in healthcare are multifaceted, encompassing privacy concerns, potential bias, and regulatory hurdles. Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive patient data is of utmost priority for businesses, necessitating robust encryption, secure storage, and strict access controls, along with patient consent and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Bias in AI algorithms, stemming from biased training data or subjective design choices, can lead to unfair and inaccurate medical outcomes, necessitating the use of diverse data sets, bias detection methods, and transparent development practices.
Privacy Concerns: Addressing Data Privacy and Security Issues
Data Sensitivity: Healthcare data is among the most sensitive types of personal information. It includes medical histories, genetic information, and other private details that require stringent protection to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Data Security: Ensuring the security of healthcare data involves implementing robust encryption, secure storage solutions, and strict access controls. This helps protect data from breaches and cyber-attacks.
Patient Consent: Obtaining informed consent from patients before collecting and using their data is crucial. Patients need to be fully aware of how their data will be used, stored, and shared.
Anonymization and De-identification: To protect patient privacy, data should be anonymized or de-identified whenever possible. This involves removing personally identifiable information (PII) so that data cannot be traced back to individual patients.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to legal frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States is essential. These regulations set standards for data protection and patient privacy that must be followed.
The Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Challenges
The evolving nature of AI technologies means that regulatory frameworks are continuously being developed and updated to address new ethical and safety concerns. Gaining approval for AI-based medical devices and software requires rigorous testing and validation processes to meet the standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States. Compliance with multiple regulatory standards across different regions further complicates the landscape, necessitating a thorough understanding of local laws, international guidelines, and industry-specific regulations.
Evolving Regulations
The regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies are continuously developing new guidelines and frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by AI technologies.
Approval Processes
Gaining regulatory approval for AI-based medical devices and software can be complex and time-consuming. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States, require rigorous testing and validation to ensure safety and efficacy.
Compliance Challenges
Ensuring compliance with multiple regulatory standards across different regions can be challenging for healthcare providers and AI developers. This includes adhering to local laws, international standards, and industry-specific regulations.
Ethical Standards
Beyond legal compliance, there is a need to establish and adhere to ethical standards for AI in healthcare. This involves balancing innovation with ethical considerations, such as patient autonomy, fairness, and the potential impact on the doctor-patient relationship.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring and post-market surveillance are necessary to ensure that AI systems remain compliant and perform as intended. This includes tracking outcomes, identifying any adverse effects, and making necessary adjustments to the AI models.
Overall, while generative AI holds tremendous potential to revolutionize healthcare, it is essential to address these ethical considerations and challenges proactively. By doing so, we can harness the power of AI to improve patient outcomes, enhance efficiency, and ensure that the benefits are realized equitably and responsibly.
Generative AI stands at the forefront of a transformative era in healthcare, promising to revolutionize how we diagnose, treat, and manage medical conditions. By enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, accelerating drug discovery, and improving patient care, AI offers unprecedented opportunities to address some of the most pressing challenges in the healthcare sector. At ACL digital, we help healthcare providers in harnessing the power of generative AI to create a more efficient, effective, and inclusive healthcare system for all. If you are a healthcare provider looking for the most effective healthcare solution, reach out to us at business@acldigital.com for more details.
Related Insights


Long Short Term Memory Networks: What It Is and How It Works?

Journey with Machine Learning towards MLOps

A Deep Dive into How Annotation Works in Machine Learning

Data Augmentation and its Importance in Machine Learning

