

ACL Digital
5 Minutes read
Revolutionizing Warehouses with AMRs & IoT Integration
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics and supply chain industry, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) integrated with IoT are revolutionizing warehouse automation, providing real-time insights and optimizing workflows. The global AMR market is projected to grow from USD 2.25 billion in 2025 to USD 4.56 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 15.1%, driven by increasing adoption in manufacturing, logistics, e-commerce, and healthcare.
Unlike traditional Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) that follow fixed paths, AMRs utilize advanced sensors, AI-driven navigation, and cameras to move autonomously within dynamic environments. Their ability to efficiently handle tasks such as picking, packing, sorting, and transporting goods minimizes manual labor, reduces errors, and speeds up warehouse processes. As businesses strive for higher efficiency and scalability, AMRs serve as a key enabler of intelligent, data-driven warehouse management.
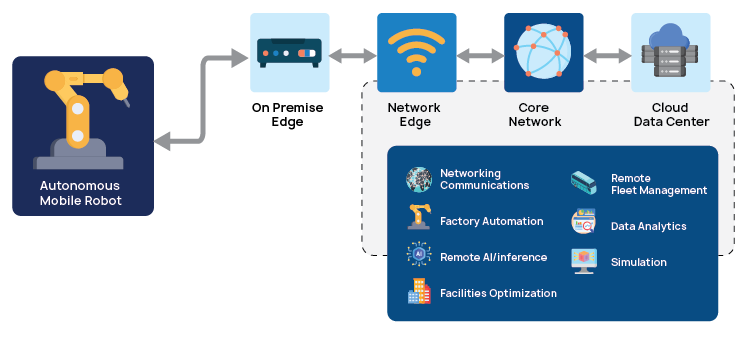
The Integration of AMR and IoT
Real-Time Monitoring and Decision-Making
IoT devices continuously gather critical warehouse data, including temperature, humidity, inventory levels, and equipment status. This real-time monitoring allows Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) to make informed decisions instantly. For example, if an IoT sensor detects a sudden temperature shift in a cold storage zone, an AMR can promptly respond to the change in temperature. AMR can move the goods that require a specific storage temperature to a section where the temperature is optimal for the goods.. This capability enhances warehouse efficiency and maintains seamless operations.
Intelligent Inventory Tracking
IoT-enabled RFID tags and smart shelving systems revolutionize inventory tracking by providing accurate, real-time data. When integrated with AMRs, these technologies create a fully automated inventory management system. AMRs autonomously navigate through storage areas, accessing live inventory data to locate, retrieve, and transport items efficiently. This integration prevents stock discrepancies, reduces stockouts and overstocking, and optimizes overall warehouse logistics.
Enhanced Safety and Risk Prevention
IoT-driven monitoring systems significantly improve workplace safety by identifying potential hazards and environmental risks in real time. For example, in an industrial environment sensors can easily detect gas leaks or temperature fluctuations and alert immediately so Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) can reroute away from dangerous areas. AMRs leverage this data to navigate around hazardous zones, reducing the likelihood of accidents. Additionally, IoT-enabled security systems allow AMRs to assist in warehouse surveillance, patrolling storage areas, detecting security breaches, and reinforcing safety protocols for a more secure operational environment.
Smart Energy Optimization for Sustainability
IoT integration plays a crucial role in energy efficiency by tracking and optimizing power consumption in warehouse operations. Sensors monitor AMR activity and automatically switch idle robots to low-power modes, preventing unnecessary energy waste. Additionally, real-time energy data allows warehouses to implement sustainable practices, such as optimizing charging schedules based on energy cost during different times of the day and conducting maintenance during off-peak hours. These measures reduce operational costs and align with corporate sustainability goals.
Seamless Workflow Coordination and Automation
IoT fosters real-time communication between AMRs and other warehouse systems, such as conveyor belts and sorting machines. This interconnectivity allows for dynamic task allocation, enabling AMRs to adjust their routes and priorities based on warehouse conditions. Automated coordination (using protocols like EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, or Modbus TCP) streamlines workflows, reduces bottlenecks, and enhances overall productivity, making warehouse logistics more agile and responsive.
How AMRs Navigate and Operate: Key Process Steps
- Sensing the Environment: AMRs use lidar, cameras, and sensors to scan and map their surroundings in real time.
- Processing and Decision-Making: AI and machine learning analyze sensor data to detect obstacles and determine the best navigation path.
- Actuation (Movement Execution): Actuators convert AI-driven decisions into physical actions like moving, turning, and stopping.
- Collaboration and Coordination: AMRs work alongside humans and other robots, ensuring efficient and safe operations.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) have revolutionized industrial automation by offering efficient, flexible, and scalable solutions across various industries. Their ability to navigate dynamic environments, integrate with existing workflows, and optimize operations makes them invaluable in modern industries. Below, we explore some of the key industrial applications and use cases of AMRs.
Manufacturing Industry
Manufacturing environments involve repetitive tasks such as material handling, assembly, and transportation. AMRs automate these processes, reducing manual labor and enhancing efficiency. They also contribute to workplace safety by taking on hazardous tasks, such as handling heavy machinery, sharp objects, or toxic substances, thereby minimizing workplace injuries.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry involves handling heavy components such as engines and chassis. AMRs equipped with lifting mechanisms and robotic arms autonomously transport these components, reducing worker strain and minimizing injury risks. They also optimize supply chain logistics by automating material flow, reducing errors, and ensuring just-in-time delivery of components and finished vehicles.
Warehousing and Logistics
AMRs have become an integral part of modern warehouses, transforming inventory management, order picking, and transportation. Businesses no longer rely solely on human workers to navigate vast storage spaces. Instead, AMRs retrieve goods, streamline restocking processes, and even assist in packaging. Their ability to work around the clock significantly enhances order fulfillment speed and operational efficiency.
Healthcare Sector
Hospitals and healthcare facilities are leveraging AMRs to optimize logistics, ensuring timely delivery of medicines, lab samples, and even meals. By reducing human intervention, AMRs improve efficiency while minimizing human errors. Additionally, during pandemics, AMRs have played a vital role in ensuring minimal human contact while maintaining operational continuity in healthcare settings.
Retail Industry
Large retail spaces are integrating AMRs for backend logistics and customer-facing tasks. In warehouses, AMRs assist in inventory management and restocking, while in-store, they guide customers to specific aisles, provide product information, and even support checkout processes. Their adoption in retail enhances both operational efficiency and customer experience.
Apparel and Fashion Logistics
Intralogistics solutions can help quick order fulfillment in the apparel industry. With AMRs
The apparel industry demands efficient intralogistics solutions for quick order fulfillment. AMRs streamline warehouse operations by automating the sorting, packing, and distribution of clothing items. Their flexibility ensures that businesses can adapt to seasonal demands and fluctuating order volumes with ease.
Smart Storage and Supermarket Logistics
Automated warehouse and logistics solutions powered by AMRs are transforming supermarket supply chains. These robots enable seamless inventory tracking, optimize space utilization, and ensure fresh product availability through efficient storage and retrieval processes.
Conclusion
The integration of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) with IoT is transforming industrial automation, warehouse logistics, and supply chain management. By leveraging real-time data, predictive analytics, and smart automation, AMRs enhance efficiency, improve safety, and enable seamless coordination across industries. Their AI-driven navigation, predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and collaborative workflows make them essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in the era of Industry 4.0.





