
N. Kranthi Kumar
9 Minutes read
Navigating the Landscape of AI Regulations
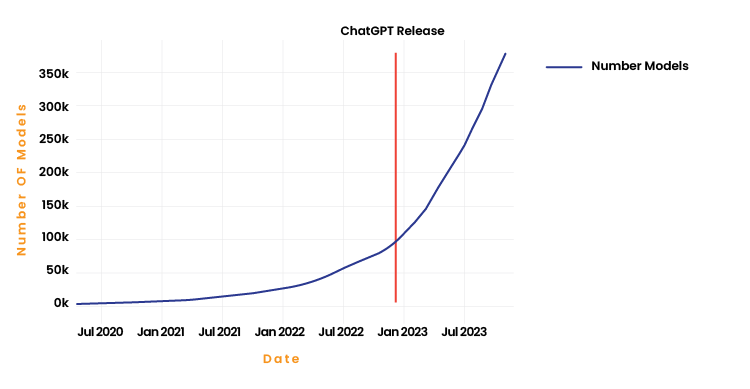
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency. However, with this rapid advancement comes the need for a robust framework to manage the risks and ensure that AI technologies are developed and deployed responsibly. The number of AI models, including Generative AI (GenAI) models, has seen an exponential rise in recent years. For instance, Hugging Face, one of the most popular open-source platforms for machine learning models, hosted approximately 950,000 models in 2024, compared to around 400,000 in 2023 and just 84,000 in 2022 (see Figure 1). This represents a massive increase in the number of models in just one year.
However, Hugging Face is not the only platform available, and many models are not open-sourced. This suggests that the total number of machine learning models globally is significantly higher. In the world of Generative AI, fine-tuned models are not always counted, but even when considering only Foundation Models, the growth has been substantial. By April 2024, there were around 330 Foundation Models, compared to just a handful in early 2023. Between September 2023 and March 2024, approximately 120 new Foundation Models were released, highlighting the rapid expansion in the GenAI space.
AI’s transformative potential is unparalleled, but with such power comes great responsibility. As companies and governments worldwide race to achieve breakthroughs in autonomous AI, the urgency for regulatory compliance has never been greater. This blog delves into the key regulations shaping the AI landscape—such as the EU AI Act, ISO/IEC 42001, and ISO/IEC 23894 and offers insights into how companies can navigate these complex requirements.
The Need for Regulatory Compliance
The race to develop autonomous AI systems is often described as the “AI Dominance War,” with companies and nations competing to achieve breakthroughs that could redefine industries. These entities are striving to create AI systems capable of operating independently, making complex decisions, and even surpassing human abilities in certain domains. However, the inherent independence of autonomous AI raises significant concerns about accountability, ethics, and safety. The push for autonomy has also exposed risks such as biased decision-making, unintended consequences, and the erosion of human oversight.
Governments and international bodies recognize that while AI has the potential to transform society positively, it also poses significant ethical and safety risks. The drive to push the boundaries of AI capabilities has necessitated regulatory oversight to ensure that these technologies are developed and deployed responsibly.

Given the rapid pace of AI innovation and the associated risks, there is a growing consensus on the need for a robust regulatory framework. Without proper oversight, the pursuit of autonomous AI could lead to unintended consequences, such as biased decision-making, job displacement, privacy violations, and even threats to public safety. Regulations are not mere bureaucratic hurdles; they are essential safeguards that align AI systems with ethical standards, human rights, and societal values.
The competition to achieve autonomous AI has led to significant advancements in Machine Learning, Robotics, Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. However, this rapid progress has also magnified the risks associated with AI systems operating without human intervention. The potential for AI to make critical decisions in areas like healthcare, transportation, or law enforcement without human oversight underscores the need for stringent regulatory measures.
For example, the EU AI Act categorizes AI systems based on their risk levels, with high-risk systems subject to rigorous compliance requirements. This approach ensures that as we advance toward more autonomous AI, these systems remain under human control, thereby maintaining accountability and minimizing the potential for harm.
Let us now explore the key aspects of the most prominent compliance and regulatory frameworks in building AI applications.
AI Regulations and Standards
Regulatory compliance and standards for AI governance and application vary widely across the globe, reflecting diverse approaches to ensuring responsible AI development and use. While some frameworks like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) play a significant role in AI governance, particularly in how AI systems handle personal data, many countries established their own regulations and standards.
In the United States, key regulations include the Algorithmic Accountability Act, a proposed legislation that mandates companies to assess the impacts of AI algorithms, particularly those affecting consumer rights. The NIST AI Risk Management Framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, offers guidelines for managing AI risks and promoting trustworthy AI systems. Additionally, the FTC Guidelines emphasize transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI usage to prevent consumer harm.
In the United Kingdom, the ICO Guidance on AI and Data Protection provides comprehensive advice on how AI systems can comply with data protection laws under the UK GDPR, ensuring that AI-driven processes respect individuals’ privacy.
India is also taking steps to regulate AI, with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) developing AI standards focused on security, privacy, and ethics. The proposed Data Protection Bill will further govern AI systems processing personal data, ensuring compliance with privacy and security requirements.
However, for the scope of this blog, we will delve deeper into three selected regulations to analyze their depth and impact: the EU AI Act, ISO/IEC 42001, and ISO/IEC 23894. These frameworks represent some of the most comprehensive and globally influential standards shaping the future of AI governance.
EU AI Act
The EU AI Act is one of the most comprehensive legislative frameworks aimed at regulating AI technologies within the European Union. It classifies AI systems into four risk categories: unacceptable risk, high risk, limited risk, and minimal risk. Unacceptable risk systems, such as those that manipulate human behavior, are banned outright. High-risk systems, like those used in critical sectors, are subject to stringent requirements, including transparency, accountability, and human oversight.
ISO/IEC 42001
ISO/IEC 42001 is an international standard that provides guidelines for managing AI systems. It emphasizes the importance of a risk management framework, encouraging organizations to assess and mitigate potential risks associated with AI. This standard is particularly valuable for companies looking to implement AI responsibly, as it provides a structured approach to identifying and addressing both ethical and operational risks.

ISO/IEC 23894
ISO/IEC 23894 focuses on the governance of AI systems, emphasizing ethical considerations. It provides guidelines to ensure that AI systems align with human rights and societal values. This standard is crucial for organizations aiming to develop AI systems that are technically sound and ethically responsible.
Key Takeaways from AI Regulations
Human-Centric AI
Regulations like the EU AI Act emphasize the importance of human oversight in AI systems, particularly those that are high-risk. Ensuring that AI systems remain under human control is essential for accountability and ethical decision-making.
Transparency and Explainability
Transparency is a recurring theme in AI regulations. Organizations must ensure that their AI systems are explainable, meaning that the decisions made by AI can be understood and scrutinized by humans. This is particularly important in sectors like healthcare and finance, where AI decisions can significantly impact individuals.
Risk Management
Both ISO/IEC 42001 and ISO/IEC 23894 highlight the need for a robust risk management framework. Companies must assess the potential risks associated with their AI systems and implement measures to mitigate these risks. This includes conducting regular audits and updating risk management strategies as AI technologies evolve.
Ethical Governance
AI systems must be governed by ethical principles that align with human rights and societal values. This includes ensuring that AI systems do not perpetuate biases or contribute to social inequalities. ISO/IEC 23894 provides a framework for ethical governance, helping organizations navigate the complex ethical landscape of AI.
Steps for Companies to Ensure Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of AI regulations requires a proactive approach. Here are some steps companies should take to ensure compliance and develop responsible AI systems:
Implement a Compliance Framework
Establish a compliance framework that aligns with relevant AI regulations. This should include regular audits, documentation of AI system processes, and a clear chain of accountability.
Invest in Explainability
Develop AI systems that are transparent and explainable. This helps in regulatory compliance and builds trust with users and stakeholders.
Adopt Ethical Guidelines
Incorporate ethical guidelines into the development and deployment of AI systems. Ensure these guidelines align with international standards like ISO/IEC 23894.
Engage in Continuous Learning
The regulatory landscape for AI is constantly evolving. It is important for companies to be informed about new regulations and standards and be prepared to adjust their systems and processes accordingly.
Collaborate with Stakeholders
Engage with regulators, industry experts, and other stakeholders to understand the implications of AI regulations and contribute to the development of best practices.
Conclusion
As we stand on the cusp of an AI-driven future, the importance of responsible development and deployment cannot be overstated. The regulations and standards discussed here represent crucial steps toward ensuring that AI technologies benefit society while minimizing potential harms.
Companies that proactively embrace these regulatory frameworks and ethical principles will not only mitigate risks but also build trust with customers, employees, and stakeholders. By fostering a culture of responsible innovation, businesses can harness the transformative power of AI while contributing to a safer, more equitable technological landscape.
The path forward requires ongoing collaboration between industry leaders, policymakers, researchers, and civil society. By working as a team, we can navigate the complexities of AI development and guarantee that AI serves the greater good of society.
For the latest updates or additional information, feel free to contact ACL Digital.





